c
Typing an Express app
Now that we have a basic understanding of how TypeScript works and how to create small projects with it, it's time to start creating something useful. We are now going to create a new project that will introduce use cases that are a little more realistic.
One major change from the previous part is that we're not going to use ts-node anymore. It is a handy tool that helps you get started, but in the long run, it is advisable to use the official TypeScript compiler that comes with the typescript npm-package. The official compiler generates and packages JavaScript files from the .ts files so that the built production version won't contain any TypeScript code anymore. This is the exact outcome we are aiming for since TypeScript itself is not executable by browsers or Node.
Setting up the project
We will create a project for Ilari, who loves flying small planes but has a difficult time managing his flight history. He is a coder himself, so he doesn't necessarily need a user interface, but he'd like to use some custom software with HTTP requests and retain the possibility of later adding a web-based user interface to the application.
Let's start by creating our first real project: Ilari's flight diaries. As usual, run npm init and install the typescript package as a dev dependency.
npm install typescript --save-devTypeScript's Native Compiler (tsc) can help us initialize our project by generating our tsconfig.json file. First, we need to add the tsc command to the list of executable scripts in package.json (unless you have installed typescript globally). Even if you installed TypeScript globally, you should always add it as a dev dependency to your project.
The npm script for running tsc is set as follows:
{
// ..
"scripts": {
"tsc": "tsc" },
// ..
}The bare tsc command is often added to scripts so that other scripts can use it, hence don't be surprised to find it set up within the project like this.
We can now initialize our tsconfig.json settings by running:
npm run tsc -- --initNote the extra -- before the actual argument! Arguments before -- are interpreted as being for the npm command, while the ones after that are meant for the command that is run through the script (i.e. tsc in this case).
The tsconfig.json file we just created contains a lengthy list of every configuration available to us. However, most of them are commented out. Studying this file can help you find some configuration options you might need. It is also completely okay to keep the commented lines, in case you might need them someday.
At the moment, we want the following to be active:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES6",
"outDir": "./build/",
"module": "commonjs",
"strict": true,
"noUnusedLocals": true,
"noUnusedParameters": true,
"noImplicitReturns": true,
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true,
"esModuleInterop": true
}
}Let's go through each configuration:
The target configuration tells the compiler which ECMAScript version to use when generating JavaScript. ES6 is supported by most browsers, so it is a good and safe option.
outDir tells where the compiled code should be placed.
module tells the compiler that we want to use CommonJS modules in the compiled code. This means we can use the old require syntax instead of the import one, which is not supported in older versions of Node.
strict is a shorthand for multiple separate options:
- noImplicitAny
- noImplicitThis
- alwaysStrict
- strictBindCallApply
- strictNullChecks
- strictFunctionTypes
- strictPropertyInitialization
They guide our coding style to use the TypeScript features more strictly. For us, perhaps the most important is the already-familiar noImplicitAny. It prevents implicitly setting type any, which can for example happen if you don't type the parameters of a function. Details about the rest of the configurations can be found in the tsconfig documentation. Using strict is suggested by the official documentation.
- noUnusedLocals prevents having unused local variables, and noUnusedParameters throws an error if a function has unused parameters.
- noImplicitReturns checks all code paths in a function to ensure they return a value.
- noFallthroughCasesInSwitch ensures that, in a switch case, each case ends either with a return or a break statement.
- esModuleInterop allows interoperability between CommonJS and ES Modules
See more in the documentation.
Now that we have set our configuration, we can continue by installing express and, of course, also @types/express. Also, since this is a real project, which is intended to be grown over time, we will use ESlint from the very beginning:
npm install express
npm install --save-dev eslint @eslint/js typescript-eslint @stylistic/eslint-plugin @types/express @types/eslint__jsNow our package.json should look like this:
{
"name": "flights",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"tsc": "tsc"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"@eslint/js": "^9.8.0",
"@stylistic/eslint-plugin": "^2.6.1",
"@types/eslint__js": "^8.42.3",
"@types/express": "^4.17.21",
"eslint": "^9.8.0",
"typescript": "^5.5.4",
"typescript-eslint": "^8.0.0"
},
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.19.2"
}
}We also create a eslint.config.mjs file with the following content:
import eslint from '@eslint/js';
import tseslint from 'typescript-eslint';
import stylistic from "@stylistic/eslint-plugin";
export default tseslint.config({
files: ['**/*.ts'],
extends: [
eslint.configs.recommended,
...tseslint.configs.recommendedTypeChecked,
],
languageOptions: {
parserOptions: {
project: true,
tsconfigRootDir: import.meta.dirname,
},
},
plugins: {
"@stylistic": stylistic,
},
rules: {
'@stylistic/semi': 'error',
'@typescript-eslint/no-unsafe-assignment': 'error',
'@typescript-eslint/no-explicit-any': 'error',
'@typescript-eslint/explicit-function-return-type': 'off',
'@typescript-eslint/explicit-module-boundary-types': 'off',
'@typescript-eslint/restrict-template-expressions': 'off',
'@typescript-eslint/restrict-plus-operands': 'off',
'@typescript-eslint/no-unused-vars': [
'error',
{ 'argsIgnorePattern': '^_' }
],
},
});Now we just need to set up our development environment, and we are ready to start writing some serious code. There are many different options for this. One option could be to use the familiar nodemon with ts-node. However, as we saw earlier, ts-node-dev does the same thing, so we will use that instead. So, let's install ts-node-dev:
npm install --save-dev ts-node-devWe finally define a few more npm scripts, and voilà, we are ready to begin:
{
// ...
"scripts": {
"tsc": "tsc",
"dev": "ts-node-dev index.ts", "lint": "eslint ." },
// ...
}As you can see, there is a lot of stuff to go through before beginning the actual coding. When you are working on a real project, careful preparations support your development process. Take the time needed to create a good setup for yourself and your team, so that everything runs smoothly in the long run.
Let there be code
Now we can finally start coding! As always, we start by creating a ping endpoint, just to make sure everything is working.
The contents of the index.ts file:
import express from 'express';
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
const PORT = 3000;
app.get('/ping', (_req, res) => {
console.log('someone pinged here');
res.send('pong');
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on port ${PORT}`);
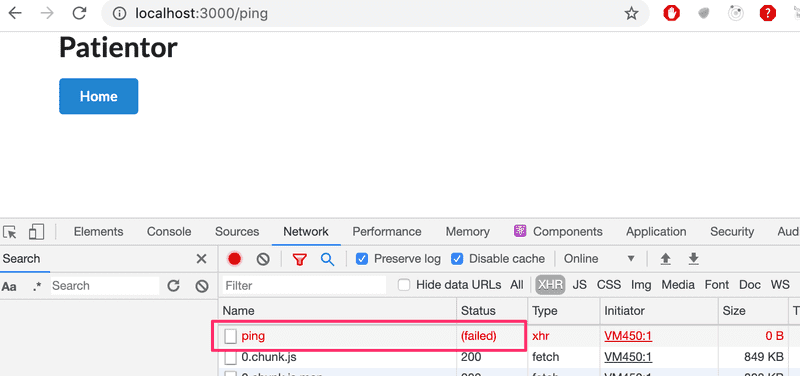
});Now, if we run the app with npm run dev, we can verify that a request to http://localhost:3000/ping gives the response pong, so our configuration is set!
When starting the app with npm run dev, it runs in development mode. The development mode is not suitable at all when we later operate the app in production.
Let's try to create a production build by running the TypeScript compiler. Since we have defined the outdir in our tsconfig.json, nothing's left but to run the script npm run tsc.
Just like magic, a native runnable JavaScript production build of the Express backend is created in file index.js inside the directory build. The compiled code looks like this
"use strict";
var __importDefault = (this && this.__importDefault) || function (mod) {
return (mod && mod.__esModule) ? mod : { "default": mod };
};
Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true });
const express_1 = __importDefault(require("express"));
const app = (0, express_1.default)();
app.use(express_1.default.json());
const PORT = 3000;
app.get('/ping', (_req, res) => {
console.log('someone pinged here');
res.send('pong');
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on port ${PORT}`);
});Currently, if we run ESlint it will also interpret the files in the build directory. We don't want that, since the code there is compiler-generated. We can prevent this in the file eslint.config.mjs as follows:
// ...
export default tseslint.config({
files: ['**/*.ts'],
extends: [
eslint.configs.recommended,
...tseslint.configs.recommendedTypeChecked,
],
languageOptions: {
parserOptions: {
project: true,
tsconfigRootDir: import.meta.dirname,
},
},
plugins: {
"@stylistic": stylistic,
},
ignores: ["build/*"], rules: {
// ...
},
});Let's add an npm script for running the application in production mode:
{
// ...
"scripts": {
"tsc": "tsc",
"dev": "ts-node-dev index.ts",
"lint": "eslint .",
"start": "node build/index.js" },
// ...
}When we run the app with npm start, we can verify that the production build also works:

Now we have a minimal working pipeline for developing our project. With the help of our compiler and ESlint, we ensure that good code quality is maintained. With this base, we can start creating an app that we could, later on, deploy into a production environment.
Implementing the functionality
Finally, we are ready to start writing some code.
Let's start from the basics. Ilari wants to be able to keep track of his experiences on his flight journeys.
He wants to be able to save diary entries, which contain:
- The date of the entry
- Weather conditions (sunny, windy, cloudy, rainy or stormy)
- Visibility (great, good, ok or poor)
- Free text detailing the experience
We have obtained some sample data, which we will use as a base to build on. The data is saved in JSON format and can be found here.
The data looks like the following:
[
{
"id": 1,
"date": "2017-01-01",
"weather": "rainy",
"visibility": "poor",
"comment": "Pretty scary flight, I'm glad I'm alive"
},
{
"id": 2,
"date": "2017-04-01",
"weather": "sunny",
"visibility": "good",
"comment": "Everything went better than expected, I'm learning much"
},
// ...
]Let's start by creating an endpoint that returns all flight diary entries.
First, we need to make some decisions on how to structure our source code. It is better to place all source code under src directory, so source code is not mixed with configuration files. We will move index.ts there and make the necessary changes to the npm scripts.
We will place all routers and modules which are responsible for handling a set of specific resources such as diaries, under the directory src/routes. This is a bit different than what we did in part 4, where we used the directory src/controllers.
The router taking care of all diary endpoints is in src/routes/diaries.ts and looks like this:
import express from 'express';
const router = express.Router();
router.get('/', (_req, res) => {
res.send('Fetching all diaries!');
});
router.post('/', (_req, res) => {
res.send('Saving a diary!');
});
export default router;We'll route all requests to prefix /api/diaries to that specific router in index.ts
import express from 'express';
import diaryRouter from './routes/diaries';const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
const PORT = 3000;
app.get('/ping', (_req, res) => {
console.log('someone pinged here');
res.send('pong');
});
app.use('/api/diaries', diaryRouter);
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on port ${PORT}`);
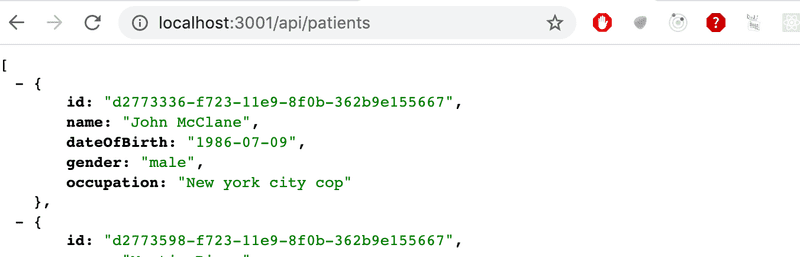
});And now, if we make an HTTP GET request to http://localhost:3000/api/diaries, we should see the message: Fetching all diaries!
Next, we need to start serving the seed data (found here) from the app. We will fetch the data and save it to data/entries.json.
We won't be writing the code for the actual data manipulations in the router. We will create a service that takes care of the data manipulation instead. It is quite a common practice to separate the "business logic" from the router code into modules, which are quite often called services. The name service originates from Domain-driven design and was made popular by the Spring framework.
Let's create a src/services directory and place the diaryService.ts file in it. The file contains two functions for fetching and saving diary entries:
import diaryData from '../../data/entries.json';
const getEntries = () => {
return diaryData;
};
const addDiary = () => {
return null;
};
export default {
getEntries,
addDiary
};But something is not right:
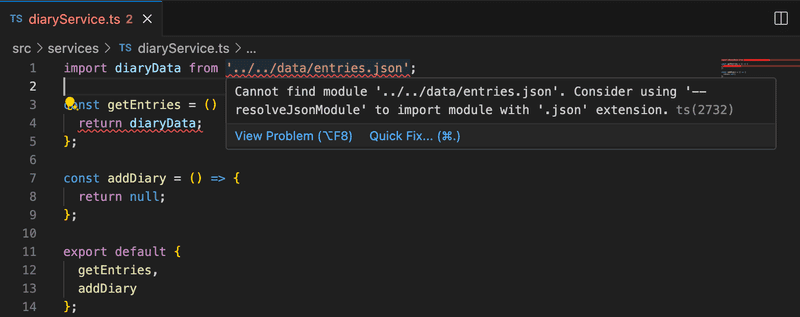
The hint says we might want to use resolveJsonModule. Let's add it to our tsconfig:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES6",
"outDir": "./build/",
"module": "commonjs",
"strict": true,
"noUnusedLocals": true,
"noUnusedParameters": true,
"noImplicitReturns": true,
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true }
}And our problem is solved.
NB: For some reason, VSCode sometimes complains that it cannot find the file ../../data/entries.json from the service despite the file existing. That is a bug in the editor, and goes away when the editor is restarted.
Earlier, we saw how the compiler can decide the type of a variable by the value it is assigned. Similarly, the compiler can interpret large data sets consisting of objects and arrays. Due to this, the compiler warns us if we try to do something suspicious with the JSON data we are handling. For example, if we are handling an array containing objects of a specific type, and we try to add an object which does not have all the fields the other objects have, or has type conflicts (for example, a number where there should be a string), the compiler can give us a warning.
Even though the compiler is pretty good at making sure we don't do anything unwanted, it is safer to define the types for the data ourselves.
Currently, we have a basic working TypeScript Express app, but there are barely any actual typings in the code. Since we know what type of data should be accepted for the weather and visibility fields, there is no reason for us not to include their types in the code.
Let's create a file for our types, types.ts, where we'll define all our types for this project.
First, let's type the Weather and Visibility values using a union type of the allowed strings:
export type Weather = 'sunny' | 'rainy' | 'cloudy' | 'windy' | 'stormy';
export type Visibility = 'great' | 'good' | 'ok' | 'poor';And, from there, we can continue by creating a DiaryEntry type, which will be an interface:
export interface DiaryEntry {
id: number;
date: string;
weather: Weather;
visibility: Visibility;
comment: string;
}We can now try to type our imported JSON:
import diaryData from '../../data/entries.json';
import { DiaryEntry } from '../types';
const diaries: DiaryEntry[] = diaryData;
const getEntries = (): DiaryEntry[] => { return diaries;};
const addDiary = () => {
return null;
};
export default {
getEntries,
addDiary
};But since the JSON already has its values declared, assigning a type for the data set results in an error:
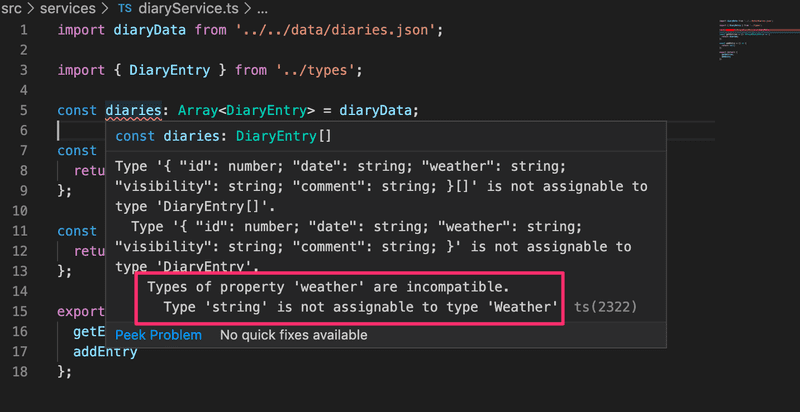
The end of the error message reveals the problem: the weather fields are incompatible. In DiaryEntry, we specified that its type is Weather, but the TypeScript compiler had inferred its type to be string.
We can fix the problem by doing a type assertion. As we already mentioned type assertions should be done only if we are certain we know what we are doing!
If we assert the type of the variable diaryData to be DiaryEntry with the keyword as, everything should work:
import diaryData from '../../data/entries.json'
import { Weather, Visibility, DiaryEntry } from '../types'
const diaries: DiaryEntry[] = diaryData as DiaryEntry[];
const getEntries = (): DiaryEntry[] => {
return diaries;
}
const addDiary = () => {
return null;
}
export default {
getEntries,
addDiary
};We should never use type assertion unless there is no other way to proceed, as there is always the danger we assert an unfit type to an object and cause a nasty runtime error. While the compiler trusts you to know what you are doing when using as, by doing this, we are not using the full power of TypeScript but relying on the coder to secure the code.
In our case, we could change how we export our data so we can type it within the data file. Since we cannot use typings in a JSON file, we should convert the JSON file to a ts file entries.ts which exports the typed data like so:
import { DiaryEntry } from "../src/types";
const diaryEntries: DiaryEntry[] = [ {
"id": 1,
"date": "2017-01-01",
"weather": "rainy",
"visibility": "poor",
"comment": "Pretty scary flight, I'm glad I'm alive"
},
// ...
];
export default diaryEntries;Now, when we import the array, the compiler interprets it correctly:
import diaries from '../../data/entries';
import { DiaryEntry } from '../types';
const getEntries = (): DiaryEntry[] => {
return diaries;
}
const addDiary = () => {
return null;
}
export default {
getEntries,
addDiary
};Note that, if we want to be able to save entries without a certain field, e.g. comment, we could set the type of the field as optional by adding ? to the type declaration:
export interface DiaryEntry {
id: number;
date: string;
weather: Weather;
visibility: Visibility;
comment?: string;}Node and JSON modules
It is important to take note of a problem that may arise when using the tsconfig resolveJsonModule option:
{
"compilerOptions": {
// ...
"resolveJsonModule": true }
}According to the node documentation for file modules, node will try to resolve modules in order of extensions:
["js", "json", "node"]In addition to that, by default, ts-node and ts-node-dev extend the list of possible node module extensions to:
["js", "json", "node", "ts", "tsx"]NB: The validity of .js, .json and .node files as modules in TypeScript depend on environment configuration, including tsconfig options such as allowJs and resolveJsonModule.
Consider a flat folder structure containing files:
├── myModule.json
└── myModule.tsIn TypeScript, with the resolveJsonModule option set to true, the file myModule.json becomes a valid node module. Now, imagine a scenario where we wish to take the file myModule.ts into use:
import myModule from "./myModule";Looking closely at the order of node module extensions:
["js", "json", "node", "ts", "tsx"]We notice that the .json file extension takes precedence over .ts and so myModule.json will be imported and not myModule.ts.
To avoid time-eating bugs, it is recommended that within a flat directory, each file with a valid node module extension has a unique filename.
Utility Types
Sometimes, we might want to use a specific modification of a type. For example, consider a page for listing some data, some of which is sensitive and some of which is non-sensitive. We might want to be sure that no sensitive data is used or displayed. We could pick the fields of a type we allow to be used to enforce this. We can do that by using the utility type Pick.
In our project, we should consider that Ilari might want to create a listing of all his diary entries excluding the comment field since, during a very scary flight, he might end up writing something he wouldn't necessarily want to show to anyone else.
The Pick utility type allows us to choose which fields of an existing type we want to use. Pick can be used to either construct a completely new type or to inform a function of what it should return on runtime. Utility types are a special kind of type, but they can be used just like regular types.
In our case, to create a "censored" version of the DiaryEntry for public displays, we can use Pick in the function declaration:
const getNonSensitiveEntries =
(): Pick<DiaryEntry, 'id' | 'date' | 'weather' | 'visibility'>[] => {
// ...
}and the compiler would expect the function to return an array of values of the modified DiaryEntry type, which includes only the four selected fields.
In this case, we want to exclude only one field, so it would be even better to use the Omit utility type, which we can use to declare which fields to exclude:
const getNonSensitiveEntries = (): Omit<DiaryEntry, 'comment'>[] => {
// ...
}To improve the readability, we should most definitively define a type alias NonSensitiveDiaryEntry in the file types.ts:
export type NonSensitiveDiaryEntry = Omit<DiaryEntry, 'comment'>;The code becomes now much more clear and more descriptive:
import diaries from '../../data/entries';
import { NonSensitiveDiaryEntry, DiaryEntry } from '../types';
const getEntries = (): DiaryEntry[] => {
return diaries;
};
const getNonSensitiveEntries = (): NonSensitiveDiaryEntry[] => { return diaries;
};
const addDiary = () => {
return null;
};
export default {
getEntries,
addDiary,
getNonSensitiveEntries};One thing in our application is a cause for concern. In getNonSensitiveEntries, we are returning the complete diary entries, and no error is given despite typing!
This happens because TypeScript only checks whether we have all of the required fields or not, but excess fields are not prohibited. In our case, this means that it is not prohibited to return an object of type DiaryEntry[], but if we were to try to access the comment field, it would not be possible because we would be accessing a field that TypeScript is unaware of even though it exists.
Unfortunately, this can lead to unwanted behavior if you are not aware of what you are doing; the situation is valid as far as TypeScript is concerned, but you are most likely allowing a use that is not wanted. If we were now to return all of the diary entries from the getNonSensitiveEntries function to the frontend, we would be leaking the unwanted fields to the requesting browser - even though our types seem to imply otherwise!
Because TypeScript doesn't modify the actual data but only its type, we need to exclude the fields ourselves:
import diaries from '../../data/entries.ts'
import { NonSensitiveDiaryEntry, DiaryEntry } from '../types'
const getEntries = () : DiaryEntry[] => {
return diaries
}
const getNonSensitiveEntries = (): NonSensitiveDiaryEntry[] => { return diaries.map(({ id, date, weather, visibility }) => ({ id, date, weather, visibility, }));};
const addDiary = () => {
return null;
}
export default {
getEntries,
getNonSensitiveEntries,
addDiary
}If we now try to return this data with the basic DiaryEntry type, i.e. if we type the function as follows:
const getNonSensitiveEntries = (): DiaryEntry[] => {we would get the following error:
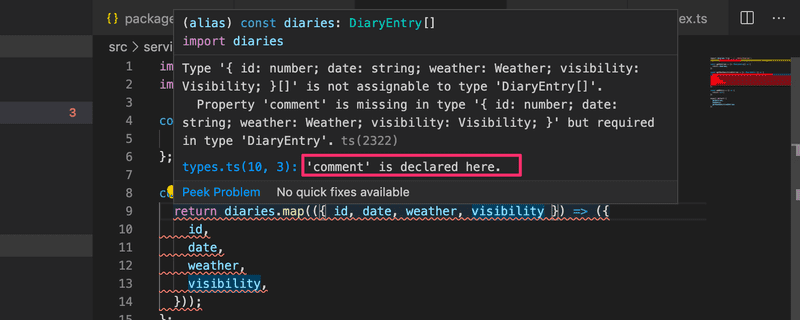
Again, the last line of the error message is the most helpful one. Let's undo this undesired modification.
Note that if you make the comment field optional (using the ? operator), everything will work fine.
Utility types include many handy tools, and it is undoubtedly worth it to take some time to study the documentation.
Finally, we can complete the route which returns all diary entries:
import express from 'express';
import diaryService from '../services/diaryService';
const router = express.Router();
router.get('/', (_req, res) => {
res.send(diaryService.getNonSensitiveEntries());});
router.post('/', (_req, res) => {
res.send('Saving a diary!');
});
export default router;The response is what we expect it to be:

Typing the request and response
So far we have not discussed anything about the types of the route handler parameters.
If we hover eg. the parameter res, we notice it has the followng type:
Response<any, Record<string, any>, number>It looks a bit weird. The type Response is a generic type that has three type parameters. If we open the type definition (by right clicking and selecting Go to Type Definition in the VS code) we see the following:
export interface Response<
ResBody = any,
LocalsObj extends Record<string, any> = Record<string, any>,
StatusCode extends number = number,
> extends http.ServerResponse, Express.Response {The first type parameter is the most interesting for us, it corresponds the response body and has a default value any. So that is why TypeScript compiler accepts any type of response and we get no help to get the response right.
We could and propably should give a proper type as the type variable. In our case it is an array of diary entries:
import { Response } from 'express'
import { NonSensitiveDiaryEntry } from "../types";
// ...
router.get('/', (_req, res: Response<NonSensitiveDiaryEntry[]>) => {
res.send(diaryService.getNonSensitiveEntries());
});
// ...If we now try to respond with wrong type of data, the code does not compile
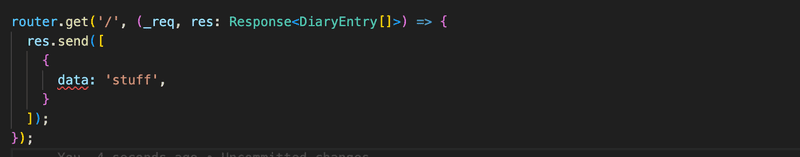
Simillarly the request parameter has the type Request that is also a generic type. We shall have a closer look on it later on.
Preventing an accidental undefined result
Let's extend the backend to support fetching one specific entry with an HTTP GET request to route api/diaries/:id.
The DiaryService needs to be extended with a findById function:
// ...
const findById = (id: number): DiaryEntry => { const entry = diaries.find(d => d.id === id); return entry;};
export default {
getEntries,
getNonSensitiveEntries,
addDiary,
findById}But once again, a new problem emerges:
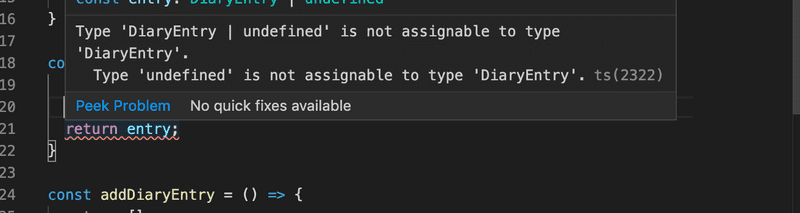
The issue is that there is no guarantee that an entry with the specified id can be found. It is good that we are made aware of this potential problem already at compile phase. Without TypeScript, we would not be warned about this problem, and in the worst-case scenario, we could have ended up returning an undefined object instead of informing the user about the specified entry not being found.
First of all, in cases like this, we need to decide what the return value should be if an object is not found, and how the case should be handled. The find method of an array returns undefined if the object is not found, and this is fine. We can solve our problem by typing the return value as follows:
const findById = (id: number): DiaryEntry | undefined => { const entry = diaries.find(d => d.id === id);
return entry;
}The route handler is the following:
import express from 'express';
import diaryService from '../services/diaryService'
router.get('/:id', (req, res) => {
const diary = diaryService.findById(Number(req.params.id));
if (diary) {
res.send(diary);
} else {
res.sendStatus(404);
}
});
// ...
export default router;Adding a new diary
Let's start building the HTTP POST endpoint for adding new flight diary entries. The new entries should have the same type as the existing data.
The code handling of the response looks as follows:
router.post('/', (req, res) => {
const { date, weather, visibility, comment } = req.body;
const addedEntry = diaryService.addDiary(
date,
weather,
visibility,
comment,
);
res.json(addedEntry);
});The corresponding method in diaryService looks like this:
import {
NonSensitiveDiaryEntry,
DiaryEntry,
Visibility, Weather} from '../types';
const addDiary = (
date: string, weather: Weather, visibility: Visibility, comment: string
): DiaryEntry => {
const newDiaryEntry = {
id: Math.max(...diaries.map(d => d.id)) + 1,
date,
weather,
visibility,
comment,
};
diaries.push(newDiaryEntry);
return newDiaryEntry;
};As you can see, the addDiary function is becoming quite hard to read now that we have all the fields as separate parameters. It might be better to just send the data as an object to the function:
router.post('/', (req, res) => {
const { date, weather, visibility, comment } = req.body;
const addedEntry = diaryService.addDiary({ date,
weather,
visibility,
comment,
}); res.json(addedEntry);
})But wait, what is the type of this object? It is not exactly a DiaryEntry, since it is still missing the id field. It could be useful to create a new type, NewDiaryEntry, for an entry that hasn't been saved yet. Let's create that in types.ts using the existing DiaryEntry type and the Omit utility type:
export type NewDiaryEntry = Omit<DiaryEntry, 'id'>;Now we can use the new type in our DiaryService, and destructure the new entry object when creating an entry to be saved:
import { NewDiaryEntry, NonSensitiveDiaryEntry, DiaryEntry } from '../types';
// ...
const addDiary = ( entry: NewDiaryEntry ): DiaryEntry => { const newDiaryEntry = {
id: Math.max(...diaries.map(d => d.id)) + 1,
...entry };
diaries.push(newDiaryEntry);
return newDiaryEntry;
};Now the code looks much cleaner!
There is still a complaint from our code:
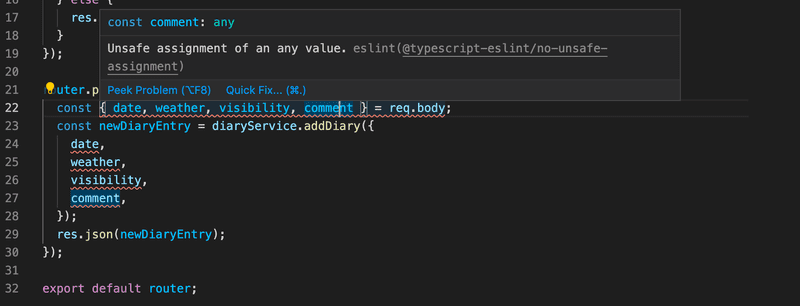
The cause is the ESlint rule @typescript-eslint/no-unsafe-assignment that prevents us from assigning the fields of a request body to variables.
For the time being, let us just ignore the ESlint rule from the whole file by adding the following as the first line of the file:
/* eslint-disable @typescript-eslint/no-unsafe-assignment */To parse the incoming data we must have the json middleware configured:
import express from 'express';
import diaryRouter from './routes/diaries';
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
const PORT = 3000;
app.use('/api/diaries', diaryRouter);
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on port ${PORT}`);
});Now the application is ready to receive HTTP POST requests for new diary entries of the correct type!
Validating requests
There are plenty of things that can go wrong when we accept data from outside sources. Applications rarely work completely on their own, and we are forced to live with the fact that data from sources outside of our system cannot be fully trusted. When we receive data from an outside source, there is no way it can already be typed when we receive it. We need to make decisions on how to handle the uncertainty that comes with this.
The disabled ESlint rule was hinting to us that the following assignment is risky:
const newDiaryEntry = diaryService.addDiary({
date,
weather,
visibility,
comment,
});We would like to have the assurance that the object in a POST request has the correct type. Let us now define a function toNewDiaryEntry that receives the request body as a parameter and returns a properly-typed NewDiaryEntry object. The function shall be defined in the file utils.ts.
The route definition uses the function as follows:
import toNewDiaryEntry from '../utils';
// ...
router.post('/', (req, res) => {
try {
const newDiaryEntry = toNewDiaryEntry(req.body);
const addedEntry = diaryService.addDiary(newDiaryEntry); res.json(addedEntry);
} catch (error: unknown) {
let errorMessage = 'Something went wrong.';
if (error instanceof Error) {
errorMessage += ' Error: ' + error.message;
}
res.status(400).send(errorMessage);
}
})We can now also remove the first line that ignores the ESlint rule no-unsafe-assignment.
Since we are now writing secure code and trying to ensure that we are getting exactly the data we want from the requests, we should get started with parsing and validating each field we are expecting to receive.
The skeleton of the function toNewDiaryEntry looks like the following:
import { NewDiaryEntry } from './types';
const toNewDiaryEntry = (object): NewDiaryEntry => {
const newEntry: NewDiaryEntry = {
// ...
};
return newEntry;
};
export default toNewDiaryEntry;The function should parse each field and make sure that the return value is exactly of type NewDiaryEntry. This means we should check each field separately.
Once again, we have a type issue: what is the type of the parameter object? Since the object is the body of a request, Express has typed it as any. Since the idea of this function is to map fields of unknown type to fields of the correct type and check whether they are defined as expected, this might be the rare case in which we want to allow the any type.
However, if we type the object as any, ESlint complains about that:
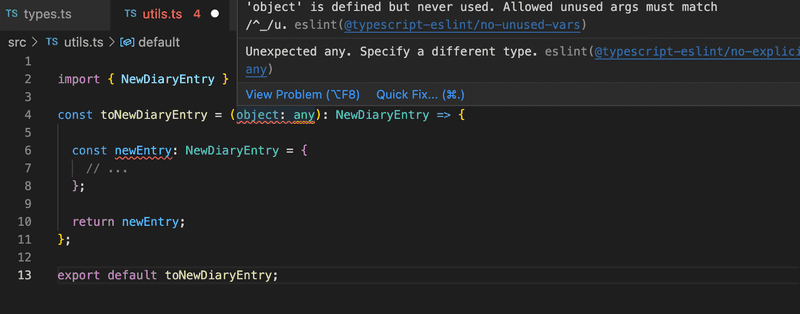
We could ignore the ESlint rule but a better idea is to follow one of the advices the editor gives in the Quick Fix and set the parameter type to unknown:
import { NewDiaryEntry } from './types';
const toNewDiaryEntry = (object: unknown): NewDiaryEntry => { const newEntry: NewDiaryEntry = {
// ...
}
return newEntry;
}
export default toNewDiaryEntry;unknown is the ideal type for our kind of situation of input validation, since we don't yet need to define the type to match any type, but can first verify the type and then confirm that is the expected type. With the use of unknown, we also don't need to worry about the @typescript-eslint/no-explicit-any ESlint rule, since we are not using any. However, we might still need to use any in some cases in which we are not yet sure about the type and need to access the properties of an object of type any to validate or type-check the property values themselves.
A sidenote from the editor
If you are like me and hate having a code in broken state for a long time due to incomplete typing, you could start by "faking" the function:
const toNewDiaryEntry = (object: unknown): NewDiaryEntry => { console.log(object); // now object is no longer unused const newEntry: NewDiaryEntry = { weather: 'cloudy', // fake the return value visibility: 'great', date: '2022-1-1', comment: 'fake news' }; return newEntry; };So before the real data and types are ready to use, I am just returning here something that has for sure the right type. The code stays in an operational state all the time and my blood pressure remains at normal levels.
Type guards
Let us start creating the parsers for each of the fields of the parameter object: unknown.
To validate the comment field, we need to check that it exists and to ensure that it is of the type string.
The function should look something like this:
const parseComment = (comment: unknown): string => {
if (!comment || !isString(comment)) {
throw new Error('Incorrect or missing comment');
}
return comment;
};The function gets a parameter of type unknown and returns it as the type string if it exists and is of the right type.
The string validation function looks like this:
const isString = (text: unknown): text is string => {
return typeof text === 'string' || text instanceof String;
};The function is a so-called type guard. That means it is a function that returns a boolean and has a type predicate as the return type. In our case, the type predicate is:
text is stringThe general form of a type predicate is parameterName is Type where the parameterName is the name of the function parameter and Type is the targeted type.
If the type guard function returns true, the TypeScript compiler knows that the tested variable has the type that was defined in the type predicate.
Before the type guard is called, the actual type of the variable comment is not known:
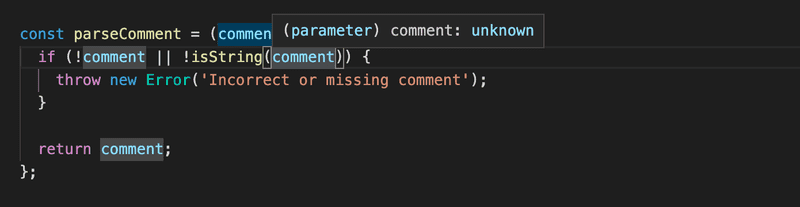
But after the call, if the code proceeds past the exception (that is, the type guard returned true), then the compiler knows that comment is of type string:
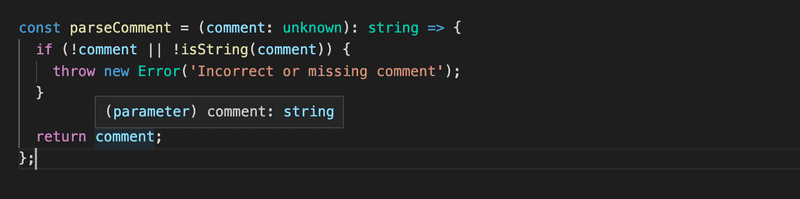
The use of a type guard that returns a type predicate is one way to do type narrowing, that is, to give a variable a more strict or accurate type. As we will soon see there are also other kind of type guards available.
Side note: testing if something is a string
Why do we have two conditions in the string type guard?
const isString = (text: unknown): text is string => { return typeof text === 'string' || text instanceof String;}Would it not be enough to write the guard like this?
const isString = (text: unknown): text is string => { return typeof text === 'string'; }Most likely, the simpler form is good enough for all practical purposes. However, if we want to be sure, both conditions are needed. There are two different ways to create string in JavaScript, one as a primitive and the other as an object, which both work a bit differently when compared to the typeof and instanceof operators:
const a = "I'm a string primitive"; const b = new String("I'm a String Object"); typeof a; --> returns 'string' typeof b; --> returns 'object' a instanceof String; --> returns false b instanceof String; --> returns trueHowever, it is unlikely that anyone would create a string with a constructor function. Most likely the simpler version of the type guard would be just fine.
Next, let's consider the date field. Parsing and validating the date object is pretty similar to what we did with comments. Since TypeScript doesn't know a type for a date, we need to treat it as a string. We should however still use JavaScript-level validation to check whether the date format is acceptable.
We will add the following functions:
const isDate = (date: string): boolean => {
return Boolean(Date.parse(date));
};
const parseDate = (date: unknown): string => {
if (!date || !isString(date) || !isDate(date)) {
throw new Error('Incorrect or missing date: ' + date);
}
return date;
};The code is nothing special. The only thing is that we can't use a type predicate based type guard here since a date in this case is only considered to be a string. Note that even though the parseDate function accepts the date variable as unknown after we check the type with isString, then its type is set as string, which is why we can give the variable to the isDate function requiring a string without any problems.
Finally, we are ready to move on to the last two types, Weather and Visibility.
We would like the validation and parsing to work as follows:
const parseWeather = (weather: unknown): Weather => {
if (!weather || !isString(weather) || !isWeather(weather)) {
throw new Error('Incorrect or missing weather: ' + weather);
}
return weather;
};The question is: how can we validate that the string is of a specific form? One possible way to write the type guard would be this:
const isWeather = (str: string): str is Weather => {
return ['sunny', 'rainy', 'cloudy', 'stormy'].includes(str);
};This would work just fine, but the problem is that the list of possible values for Weather does not necessarily stay in sync with the type definitions if the type is altered. This is most certainly not good, since we would like to have just one source for all possible weather types.
Enum
In our case, a better solution would be to improve the actual Weather type. Instead of a type alias, we should use the TypeScript enum, which allows us to use the actual values in our code at runtime, not only in the compilation phase.
Let us redefine the type Weather as follows:
export enum Weather {
Sunny = 'sunny',
Rainy = 'rainy',
Cloudy = 'cloudy',
Stormy = 'stormy',
Windy = 'windy',
}Now we can check that a string is one of the accepted values, and the type guard can be written like this:
const isWeather = (param: string): param is Weather => {
return Object.values(Weather).map(v => v.toString()).includes(param);
};Note that we need to take the string representation of the enum values for the comparison, that is why we do the mapping.
One issue arises after these changes. Our data in file data/entries.ts does not conform to our types anymore:
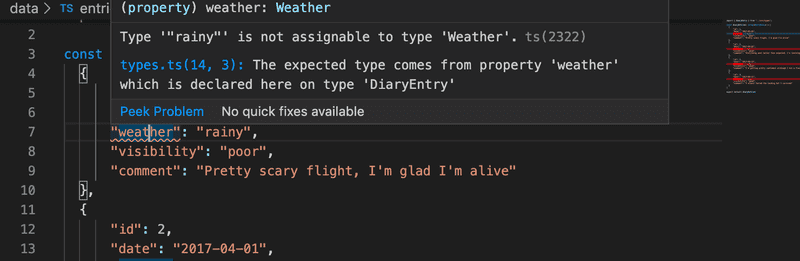
This is because we cannot just assume a string is an enum.
We can fix this by mapping the initial data elements to the DiaryEntry type with the toNewDiaryEntry function:
import { DiaryEntry } from "../src/types";
import toNewDiaryEntry from "../src/utils";
const data = [
{
"id": 1,
"date": "2017-01-01",
"weather": "rainy",
"visibility": "poor",
"comment": "Pretty scary flight, I'm glad I'm alive"
},
// ...
]
const diaryEntries: DiaryEntry [] = data.map(obj => {
const object = toNewDiaryEntry(obj) as DiaryEntry;
object.id = obj.id;
return object;
});
export default diaryEntries;Note that since toNewDiaryEntry returns an object of type NewDiaryEntry, we need to assert it to be DiaryEntry with the as operator.
Enums are typically used when there is a set of predetermined values that are not expected to change in the future. Usually, they are used for much tighter unchanging values (for example, weekdays, months, cardinal directions), but since they offer us a great way to validate our incoming values, we might as well use them in our case.
We still need to give the same treatment to Visibility. The enum looks as follows:
export enum Visibility {
Great = 'great',
Good = 'good',
Ok = 'ok',
Poor = 'poor',
}The type guard and the parser are below:
const isVisibility = (param: string): param is Visibility => {
return Object.values(Visibility).map(v => v.toString()).includes(param);
};
const parseVisibility = (visibility: unknown): Visibility => {
if (!visibility || !isString(visibility) || !isVisibility(visibility)) {
throw new Error('Incorrect or missing visibility: ' + visibility);
}
return visibility;
};And finally, we can finalize the toNewDiaryEntry function that takes care of validating and parsing the fields of the POST body. There is however one more thing to take care of. If we try to access the fields of the parameter object as follows:
const toNewDiaryEntry = (object: unknown): NewDiaryEntry => {
const newEntry: NewDiaryEntry = {
comment: parseComment(object.comment),
date: parseDate(object.date),
weather: parseWeather(object.weather),
visibility: parseVisibility(object.visibility)
};
return newEntry;
};we notice that the code does not compile. This is because the unknown type does not allow any operations, so accessing the fields is not possible.
We can again fix the problem by type narrowing. We have now two type guards, the first checks that the parameter object exists and it has the type object. After this, the second type guard uses the in operator to ensure that the object has all the desired fields:
const toNewDiaryEntry = (object: unknown): NewDiaryEntry => {
if ( !object || typeof object !== 'object' ) {
throw new Error('Incorrect or missing data');
}
if ('comment' in object && 'date' in object && 'weather' in object && 'visibility' in object) {
const newEntry: NewDiaryEntry = {
weather: parseWeather(object.weather),
visibility: parseVisibility(object.visibility),
date: parseDate(object.date),
comment: parseComment(object.comment)
};
return newEntry;
}
throw new Error('Incorrect data: some fields are missing');
};If the guard does not evaluate to true, an exception is thrown.
The use of the operator in actually now guarantees that the fields indeed exist in the object. Because of that, the existence checks in the parsers are no longer needed:
const parseVisibility = (visibility: unknown): Visibility => {
// check !visibility removed:
if (!isString(visibility) || !isVisibility(visibility)) {
throw new Error('Incorrect visibility: ' + visibility);
}
return visibility;
};If a field, e.g. comment would be optional, the type narrowing should take that into account, and the operator in could not be used quite as we did here, since the in test requires the field to be present.
If we now try to create a new diary entry with invalid or missing fields, we are getting an appropriate error message:
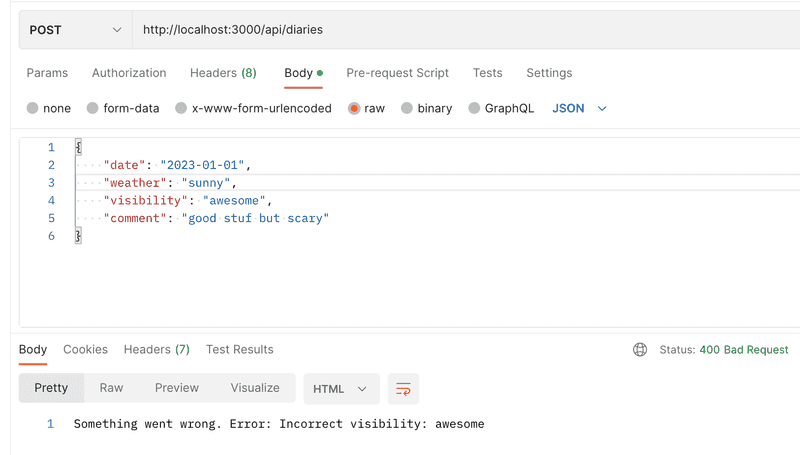
The source code of the application can be found on GitHub.
Using schema validation libraries
Writing a validator to the request body can be a huge burden. Thankfully there exists several schema validator libraries that can help. Let us now have a look at Zod that works pretty well with TypeScript.
Let us get started:
npm install zodParsers of the primitive valued fields such as
const isString = (text: unknown): text is string => {
return typeof text === 'string' || text instanceof String;
};
const parseComment = (comment: unknown): string => {
if (!isString(comment)) {
throw new Error('Incorrect comment');
}
return comment;
};are easy to replace as follows:
const parseComment = (comment: unknown): string => {
return z.string().parse(comment);};First the string method of Zod is used to define the required type (or schema in Zod terms). After that the value (which is of the type unknown) is parsed with the method parse, which returns the value in the required type or throws an exception.
We do not actually need the helper function parseComment anymore and can use the Zod parser directly:
export const toNewDiaryEntry = (object: unknown): NewDiaryEntry => {
if ( !object || typeof object !== 'object' ) {
throw new Error('Incorrect or missing data');
}
if ('comment' in object && 'date' in object && 'weather' in object && 'visibility' in object) {
const newEntry: NewDiaryEntry = {
weather: parseWeather(object.weather),
visibility: parseVisibility(object.visibility),
date: parseDate(object.date),
comment: z.string().parse(object.comment) };
return newEntry;
}
throw new Error('Incorrect data: some fields are missing');
};Zod has a bunch of string specific validations, eg. one that validates if a string is a valid date, so we get also rid of the date field parser:
export const toNewDiaryEntry = (object: unknown): NewDiaryEntry => {
if ( !object || typeof object !== 'object' ) {
throw new Error('Incorrect or missing data');
}
if ('comment' in object && 'date' in object && 'weather' in object && 'visibility' in object) {
const newEntry: NewDiaryEntry = {
weather: parseWeather(object.weather),
visibility: parseVisibility(object.visibility),
date: z.string().date().parse(object.date), comment: z.string().optional().parse(object.comment) };
return newEntry;
}
throw new Error('Incorrect data: some fields are missing');
};We have also made the field comment optional since it is defined optional in the TypeScript definition.
Zod has also support for enums and thanks to that our code simplifies further:
export const toNewDiaryEntry = (object: unknown): NewDiaryEntry => {
if ( !object || typeof object !== 'object' ) {
throw new Error('Incorrect or missing data');
}
if ('comment' in object && 'date' in object && 'weather' in object && 'visibility' in object) {
const newEntry: NewDiaryEntry = {
weather: z.nativeEnum(Weather).parse(object.weather), visibility: z.nativeEnum(Visibility).parse(object.visibility), date: z.string().date().parse(object.date),
comment: z.string().optional().parse(object.comment)
};
return newEntry;
}
throw new Error('Incorrect data: some fields are missing');
};We have so far just used Zod to parse the type or schema of individual fields, but we can go one step further and define the whole new diary entry as a Zod object schema:
const newEntrySchema = z.object({
weather: z.nativeEnum(Weather),
visibility: z.nativeEnum(Visibility),
date: z.string().date(),
comment: z.string().optional()
});Now it is just enough to call parse of the defined schema:
export const toNewDiaryEntry = (object: unknown): NewDiaryEntry => {
return newEntrySchema.parse(object);
};With the help from documentation we could also improve the error handling:
router.post('/', (req, res) => {
try {
const newDiaryEntry = toNewDiaryEntry(req.body);
const addedEntry = diaryService.addDiary(newDiaryEntry);
res.json(addedEntry);
} catch (error: unknown) {
if (error instanceof z.ZodError) { res.status(400).send({ error: error.issues }); } else { res.status(400).send({ error: 'unknown error' }); } }
});The response in case of error looks pretty good:
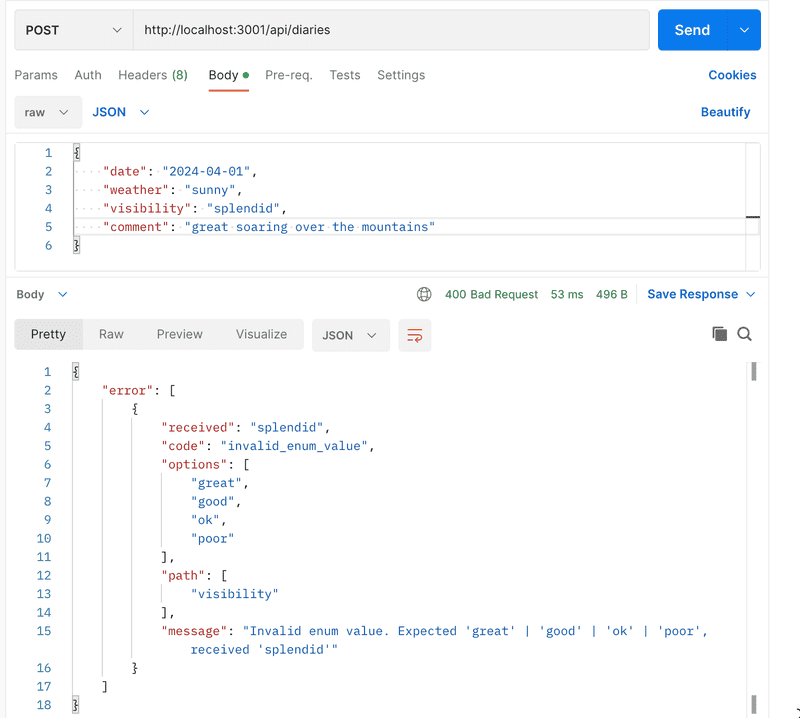
We could develop our solution still some steps further. Our type definitions currently look like this:
export interface DiaryEntry {
id: number;
date: string;
weather: Weather;
visibility: Visibility;
comment?: string;
}
export type NewDiaryEntry = Omit<DiaryEntry, 'id'>;So besides the type NewDiaryEntry we have also the Zod schema NewEntrySchema that defines the shape of a new entry. We can use the schema to infer the type:
import { z } from 'zod';
import { newEntrySchema } from './utils'
export interface DiaryEntry {
id: number;
date: string;
weather: Weather;
visibility: Visibility;
comment?: string;
}
// infer the type from schema
export type NewDiaryEntry = z.infer<typeof newEntrySchema>; We could take this even a bit further and define the DiaryEntry based on NewDiaryEntry:
export type NewDiaryEntry = z.infer<typeof newEntrySchema>;
export interface DiaryEntry extends NewDiaryEntry {
id: number;
}This would remove all the duplication in the type and schema definitions but feels a bit backward so we decide to define the type DiaryEntry explicitly with TypeScript.
Unfortunately the opposite is not possible: we can not define the Zod schema based on TypeScript type definitions, and due to this, the duplication in the type and schema definitions is hard to avoid.
The current state of the source code can be found in the part2 branch of this GitHub repository.
Parsing request body in middleware
We can now get rid of this method altogether
export const toNewDiaryEntry = (object: unknown): NewDiaryEntry => {
return newEntrySchema.parse(object);
};and just call the Zod-parser directly in the route handler:
import express, { Request, Response } from 'express';
import diaryService from '../services/diaryService';
import { NewEntrySchema } from '../utils';
router.post('/', (req, res) => { try {
const newDiaryEntry = NewEntrySchema.parse(req.body); const addedEntry = diaryService.addDiary(newDiaryEntry);
res.json(addedEntry);
} catch (error: unknown) {
if (error instanceof z.ZodError) {
res.status(400).send({ error: error.issues });
} else {
res.status(400).send({ error: 'unknown error' });
}
}
});Instead of calling the request body parsing method explicitly in the route handler, the validation of the input could also be done in a middleware function.
We have also added the type definitions to the route handler parameters, and shall also use types in the middleware function newDiaryParser:
const newDiaryParser = (req: Request, _res: Response, next: NextFunction) => {
try {
NewEntrySchema.parse(req.body);
next();
} catch (error: unknown) {
next(error);
}
};The middleware just calls the schema parser to the request body. If the parsing throws an exception, that is passed to the error handling middleware.
So after the request passes this middleware, it is known that the request body is a proper new diary entry. We can tell this fact to TypeScript compiler by giving a type parameter to the Request type:
router.post('/', newDiaryParser, (req: Request<unknown, unknown, NewDiaryEntry>, res: Response<DiaryEntry>) => { const addedEntry = diaryService.addDiary(req.body); res.json(addedEntry);
});Thanks to the middleware, the request body is now known to be of right type and it can be directly given as parameter to the function diaryService.addDiary.
The syntax of the Request<unknown, unknown, NewDiaryEntry> looks a bit odd. The Request is a generic type with several type parameters. The third type parameter represents the request body, and in order to give it the value NewDiaryEntry we have to give some value to the two first parameters. We decide to define those unknown since we do not need those for now.
Since the possible errors in validation are now handled in the error handling middleware, we need to define one that handles the Zod errors properly:
const errorMiddleware = (error: unknown, _req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) => {
if (error instanceof z.ZodError) {
res.status(400).send({ error: error.issues });
} else {
next(error);
}
};
router.post('/', newDiaryParser, (req: Request<unknown, unknown, NewDiaryEntry>, res: Response<DiaryEntry>) => {
// ...
});
router.use(errorMiddleware);The final version of the source code can be found in the part3 branch of this GitHub repository.